Near Field Communication, or NFC, is a powerful technology packed into many modern Android devices, yet often remains underutilized. This practical guide delves into the world of NFC on your Android device, providing clear instructions and real-world examples to unlock its full potential. Learn how to leverage NFC for everything from simple tasks like mobile payments and sharing data to more advanced applications like automating your home environment. This guide serves as a starting point for understanding the capabilities of NFC and how it can seamlessly integrate into your daily life with your Android device.
From the basics of enabling NFC on your Android device to exploring the various NFC tags and their uses, this guide covers it all. Discover how to use NFC for quickly connecting to Bluetooth devices, launching apps, and even configuring device settings with a single tap. Explore the security aspects of NFC and learn how to safeguard your information while taking advantage of this convenient technology. Prepare to discover the transformative power of NFC and how it can simplify and enhance your experience with your Android device.
Understanding NFC Technology and Its Capabilities
Near-field communication (NFC) is a short-range wireless technology that allows devices to communicate with each other when they are held close together. It operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz and has a typical range of up to 4 centimeters.
NFC is based on the principles of radio-frequency identification (RFID), but with a more limited range. This limited range enhances security, making it suitable for applications like contactless payments and secure data transfer.
NFC offers several key capabilities:
- Reader/Writer Mode: An NFC-enabled device can read data from passive NFC tags or write data to them. This is commonly used for accessing information from smart posters or interacting with NFC-enabled products.
- Peer-to-Peer Mode: Two NFC-enabled devices can exchange data directly with each other. This enables features like sharing files or contact information.
- Card Emulation Mode: An NFC-enabled device can emulate a contactless smart card, allowing it to be used for payments or access control systems.
Understanding these core functionalities lays the groundwork for utilizing NFC effectively on your Android device.
Checking for NFC Compatibility on Your Android Device
Before diving into the world of NFC, it’s essential to verify if your Android device supports this technology. Most modern Android smartphones include NFC, but older models may not. Here’s how to check:
Method 1: Checking System Settings
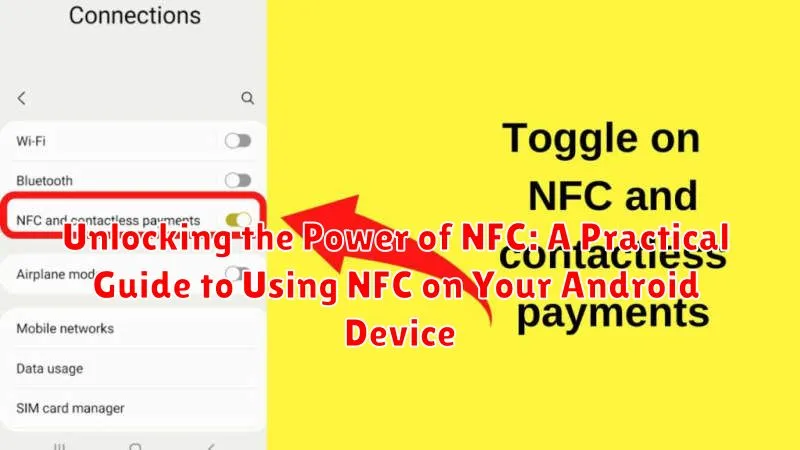
The most straightforward method is to look within your device’s settings. Open the Settings app. Look for “Connected devices” or a similar entry. Within this section, you should see “Connection preferences“, “NFC“, or a related option. If you see an NFC toggle or menu, your device is NFC-enabled.
Method 2: Quick Settings Panel
On many Android devices, a quick check can be performed via the quick settings panel. Swipe down from the top of your screen to access the quick settings tiles. Look for an NFC icon. Its presence indicates NFC compatibility.
If you can’t find any NFC-related options in either location, your device likely doesn’t have NFC functionality.
Enabling NFC and Adjusting Settings
Once you’ve confirmed your Android device’s NFC compatibility, the next step is to enable the technology and configure its settings. The process may vary slightly depending on your device’s manufacturer and Android version, but the general steps are similar.
Typically, you can find the NFC control within the “Wireless & networks” or “Connected devices” section of your device’s settings. Look for an option labeled “NFC” and toggle it on.
In some cases, you might find additional settings related to NFC, such as “Android Beam” (for older Android versions) or options related to contactless payments. If you intend to use NFC for payments, ensure the relevant settings are configured correctly based on your payment provider’s instructions.
After enabling NFC, it’s a good practice to test its functionality. You can do this by bringing your device close to another NFC-enabled device or an NFC tag. A sound or vibration usually indicates successful NFC communication. You can further adjust settings related to specific NFC applications within those respective apps.
Pairing and Connecting with NFC-Enabled Devices
NFC simplifies pairing and connecting with various devices, eliminating the need for complex setup procedures. This section outlines how to connect your Android device to NFC-compatible Bluetooth speakers, headphones, and other devices.
First, ensure both devices are powered on and have NFC enabled. Locate the NFC touchpoint on each device. This is usually indicated by the NFC logo. Gently tap the back of your Android phone against the NFC touchpoint of the other device.
Your phone should vibrate or provide an audible notification, indicating a successful connection attempt. Follow any on-screen prompts to confirm the pairing. Once connected, you can enjoy seamless audio streaming or other functionalities provided by the paired device.
Some devices might require a specific app for initial setup or extended functionality. Refer to the device’s user manual for detailed instructions if needed.
Sharing Files and Data Wirelessly with Android Beam

Android Beam leverages NFC to facilitate quick and easy sharing of various types of data between compatible devices. This feature simplifies the process of transferring information without the need for cables or complex setups.
Sharing Procedure: To initiate a transfer, ensure both devices have NFC enabled and Android Beam activated. Simply place the backs of the two devices together. Once a connection is established, you’ll feel a slight vibration or hear a sound.
Supported File Types: Android Beam supports a range of file types including photos, videos, web pages, and contact information. The specific data that can be shared might vary based on the apps installed on your device and the receiving device’s capabilities.
Initiating the Transfer: After the devices connect, a preview of the content to be shared will appear on the sending device’s screen. Tap the screen to confirm and initiate the transfer. The receiving device will then receive the data.
Troubleshooting: If you experience difficulties with Android Beam, ensure both devices support the feature and that their backs are correctly aligned. Check that NFC is enabled and that your device’s screen is unlocked.
Making Mobile Payments with NFC (e.g., Google Wallet)
NFC technology has revolutionized how we make payments, offering a secure and convenient alternative to traditional methods. With services like Google Wallet, you can simply tap your phone to a compatible terminal and complete your purchase.
Setting up mobile payments is typically straightforward. First, ensure NFC is enabled in your device’s settings. Then, you’ll need to add your credit or debit card information to your chosen payment app, such as Google Wallet. This usually involves entering your card number, expiration date, and security code.
At the checkout, look for the contactless payment symbol on the terminal. Once prompted, unlock your phone and hold it near the reader. A vibration or sound will usually confirm the transaction. For added security, some devices may require fingerprint authentication or a PIN entry.
Mobile payments offer several benefits including speed and ease of use. You no longer need to carry physical cards, reducing the risk of loss or theft. Furthermore, the technology incorporates robust security measures to protect your financial information.
Automating Tasks with NFC Tags and Apps
NFC tags offer a powerful way to automate everyday tasks on your Android device. These small, programmable tags can be easily purchased and configured to trigger specific actions when tapped with your phone.
Setting up automated tasks typically involves using a dedicated NFC tag writing app. These apps allow you to write specific commands or data onto the NFC tag. You can then place these tags strategically around your home, office, or car.
Example applications include:
- Launching a specific app: Tap a tag to automatically open your navigation app when entering your car.
- Connecting to Wi-Fi: Simplify guest Wi-Fi access by programming a tag with your network credentials.
- Controlling smart home devices: Turn on lights or adjust the thermostat with a simple tap.
- Setting phone profiles: Switch to silent mode when entering a meeting room.
Choosing the right NFC tag depends on the intended application. Consider factors like read range and memory capacity when making your selection.
Troubleshooting Common NFC Connectivity Issues
While NFC is generally reliable, occasional connectivity problems can arise. Here’s a breakdown of common issues and their solutions:
NFC Isn’t Turning On
Ensure NFC is enabled in your device’s settings. Look for “Connected devices” or a similar category. Restarting your device can sometimes resolve software glitches preventing NFC activation.
Device Not Reading Tags or Making Payments
Check your phone’s case. Thick or metallic cases can interfere with NFC communication. Try removing the case temporarily. Ensure the NFC antenna is located correctly. Consult your device’s manual to identify its placement and hold your phone accordingly against the reader or tag.
Slow or Intermittent Connection
Clean the NFC antenna area on your phone. Dust or debris can impede the signal. Gently wipe it with a clean, dry cloth. Try holding your device closer and steadier against the reader or tag for a more consistent connection. Avoid moving the device during the transaction.
App-Specific NFC Issues
If problems occur within a specific app, ensure the app has the necessary NFC permissions. Check the app’s settings or your device’s app permissions manager. Reinstalling the app can sometimes resolve underlying software conflicts.
Exploring Advanced NFC Applications

Beyond mobile payments and simple task automation, NFC offers a range of advanced applications that showcase its versatility. These applications leverage the close-proximity interaction enabled by NFC to provide unique functionalities and experiences.
Connecting to Devices
NFC can simplify pairing with Bluetooth and Wi-Fi devices. Tapping your phone to an NFC-enabled speaker or headphone can initiate the pairing process, eliminating the need for manual searches and passcode entries.
Interactive Experiences
NFC tags embedded in museum exhibits or product displays can provide contextual information directly to a user’s smartphone. This interactive element enhances engagement and provides a more immersive experience.
Access Control
NFC can be used for secure access control to buildings, offices, or even vehicles. NFC-enabled keycards or smartphone credentials offer a convenient and reliable alternative to traditional keys.
Ensuring Security and Privacy When Using NFC
While NFC offers incredible convenience, it’s crucial to be aware of potential security and privacy risks. Understanding these risks and taking appropriate precautions can significantly enhance your NFC experience.
Be mindful of unintended taps. Keep your phone secure and avoid accidentally tapping against unknown NFC tags or readers. Malicious actors could potentially use strategically placed tags to extract information or install malware.
Review app permissions carefully. Before installing any NFC-enabled app, examine the permissions it requests. Only grant access to permissions that are absolutely necessary for the app’s functionality. Overly permissive apps could potentially compromise your data.
Keep your phone’s software updated. Regularly updating your Android operating system and apps ensures you have the latest security patches, protecting you from known vulnerabilities that could be exploited via NFC.
Use strong passwords and lock screen security. Implementing a strong lock screen password or biometric authentication provides an additional layer of security, preventing unauthorized access to your device and NFC functionalities should your phone be lost or stolen.